Removing harmful race-based clinical algorithms: A toolkit

Step 2-Readiness & needs assessment
The goal of Step 2 is to evaluate your institution’s current capacity to remove harmful race-based clinical algorithms and benchmark your knowledge, education, resources, and integration capabilities.
Follow the activities below and use the Readiness Self-Assessment to determine your level of readiness to de-implement harmful race-based clinical algorithms.
Important stakeholders
All stakeholders necessary for the assessment, including executive and health equity leadership, clinical care providers, IT and data teams, and non-clinical personnel with expertise related to policies, operations, training, and education, who will provide insight into institutional readiness and areas for improvement.
Complete these activities
To achieve this goal, complete the following activities:
1. Convene representative stakeholders
Convene all necessary stakeholders identified in the “Important stakeholders” section to ensure representativeness and completeness of the institution’s Readiness Self-Assessment.
2. Involve providers in the assessment
In the assessment process, involve providers through focus groups, interviews, and surveys to identify strengths and gaps in their current training and education related to race-conscious medicine.
3. Examine patient data
Review institutional patient data to examine how race, ethnicity, and other demographic data are collected, stored, and related to health outcomes.
4. Use the Readiness Self-Assessment
Conduct your Readiness Self-Assessment to evaluate the institution’s readiness across the Maturity Model’s levels of nascent, initial, active, and sustained readiness, identifying needs and gaps in key areas that affect the ability to comprehensively de-implement harmful race-based algorithms.
5. Develop an action plan
Develop an action plan based on the assessment results, identifying institutional barriers and facilitators, and outlining steps to advance to Step 3 and/or increase readiness by addressing needs identified in Step 2 of the toolkit.
6. Develop your fundraising strategy
Based on the results of the assessment, develop a fundraising strategy to secure resources to support progress toward Step 3 and/or facilitate ongoing efforts to advance readiness in Step 2 of the toolkit.
Take the Readiness Self-Assessment
Use this Readiness Self-Assessment to determine your level of readiness to de-implement harmful race-based clinical algorithms. Your assessment results will provide recommendations for increasing readiness for continuous improvement.
Explore further by hovering over the (+) sign.
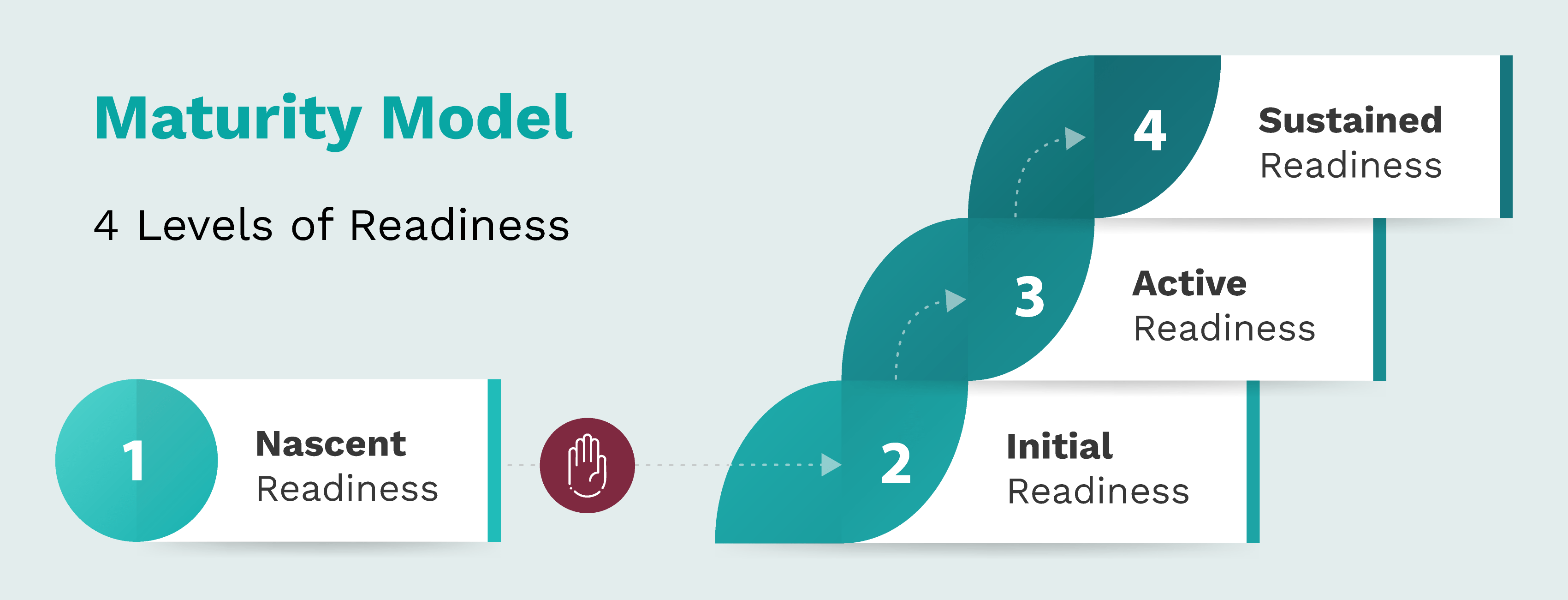
Level 1: Nascent Readiness
Individual champions build awareness of harmful race-based algorithms, but without dedicated resources and with immature data infrastructure limiting work plan development, education, and engagement efforts.
Level 2: Initial Readiness
Key stakeholders are engaged and committed, and foundational resources, policies, and data systems are in place. The institution is prepared to complete the de-implementation of at least one harmful race-based algorithm, including initial provider education and patient engagement efforts.
Level 3: Active Readiness
Widespread buy-in, dedicated resources, and formal work plans are in place for scaled de-implementation of multiple harmful race-based algorithms, supported by comprehensive provider education and patient engagement initiatives.
Level 4: Sustained Readiness
Demonstrated commitment to continuous program improvement and advanced data-driven practices facilitates seamless harmful algorithm de-implementation and workflow integration, fosters measurable health equity outcome improvements and restorative actions, and positions the institution to lead collective action across the ecosystem.
PAUSE:
Before proceeding, it is recommended to focus on strengthening team preparation in Step 1, then revisit the Readiness Self-Assessment in Step 2. De-implementation should not begin until your institution reaches at least Level 2: Initial Readiness, ensuring sufficient commitment, resources, data, and education and engagement initiatives to support a comprehensive, patient-centered process.
Read more about the levels of readiness that inform the Maturity Model here
Readiness Self-Assessment
Recommendations for increasing readiness
- Progressing from Level 1 to Level 2
- Progressing from Level 2 to Level 3
- Progressing from Level 3 to Level 4
Progressing from Level 1 to Level 2
To transition from nascent to initial readiness and de-implement their first harmful race-based algorithm, institutions should cultivate engagement among key stakeholders and leaders, identify available resources, and begin developing foundational policies and data systems.
- Core knowledge and commitment: Facilitate discussions among key stakeholders and leaders to explore the potential harms of race-based clinical algorithms in practice.
- Education and engagement: Initiate provider education and patient engagement initiatives to address implicit bias and medical racism, and begin planning for enforcement and tracking.
- Resources and policies: Identify initial resources from established, broad health equity initiatives to begin addressing algorithmic bias at your institution.
- Implementation and integration: Begin developing informal work plans to identify harmful uses of race in healthcare decision-making at the institution and document the implications on patient care.
- Data and measurement: Establish consistent practices for collecting race and ethnicity data across the institution.
Progressing from Level 2 to Level 3
To progress from initial to active readiness, institutions should identify an executive champion, allocate dedicated resources, and formalize policies and work plans to enable the de-implementation of multiple harmful race-based algorithms.
- Core knowledge and commitment: Secure the commitment of an executive champion who will lead institutional efforts to remove racial bias from clinical algorithms.
- Education and engagement: Implement comprehensive provider education and patient engagement strategies that include specific enforcement and accountability mechanisms.
- Resources and policies: Dedicate resources and formalize policies that will support the de-implementation of harmful race-based clinical algorithms at the institution.
- Implementation and integration: Create a formal work plan for integrating race-conscious algorithms and more nuanced shared decision-making approaches into electronic health records and clinical workflows.
- Data and measurement: Standardize race and ethnicity data collection and invest in the infrastructure needed to consistently stratify patient outcomes by race, ethnicity, and social determinants of health.
Progressing from Level 3 to Level 4
To advance from active to sustained readiness, institutions must demonstrate their commitment to program improvement and collective action across the ecosystem, through advanced data practices and seamless workflow integrations that lead to measurable improvements in health equity outcomes, including restorative actions.
- Core knowledge and commitment: Promote a deep appreciation of the historical context and challenges of harmful race modifiers across all levels of the organization.
- Education and engagement: Make provider education on algorithmic bias and health equity mandatory and ongoing and formalize patient engagement through a standardized framework emphasizing restorative justice.
- Resources and policies: Dedicate staff, funding, and policies to ensure program sustainability and active participation in efforts to advance health equity initiatives across the healthcare ecosystem.
- Implementation and integration: Eliminate harmful race modifiers and replace them with race-conscious, shared decision-making approaches that are seamless, standardized, and guided by best practices.
- Data and measurement: Build a robust data infrastructure that incorporates comprehensive metrics, including race, ethnicity, insurance status, age, geography, zip code, language, and genomics.
Next steps
Once you have completed these activities, you will receive results that will highlight your institution’s strengths and pinpoint gaps in your readiness. This will help you create a clear roadmap to address the needs within Step 2 and prepare for de-implementation in the subsequent steps of the toolkit.



